Ever wondered how the blockchain, once just a glimmer in the eye of a mysterious figure named Satoshi Nakamoto, has evolved into the financial powerhouse it is today? The secret sauce lies in consensus mechanisms, the unsung heroes of the crypto world. These mechanisms are the digital equivalent of a well-oiled machine, ensuring everyone plays nice in the decentralized sandbox. From Bitcoin’s Proof of Work (PoW) to XRP’s Consensus Protocol, the evolution of these mechanisms tells a tale of innovation, competition, and a little bit of friendly rivalry. So, buckle up, dear reader, as we journey through the fascinating world of blockchain validation methods.
Let’s start at the beginning—Bitcoin’s Proof of Work, the granddaddy of consensus mechanisms. This method is like the high school jock who benches the most weight but eats up all your snacks (or, in this case, energy). While PoW brought us the first decentralized cryptocurrency and laid the groundwork for countless innovations, it’s also notorious for being an energy guzzler. Is it sustainable? That’s the million-dollar question—or perhaps, the 1 Bitcoin question, given current market fluctuations!
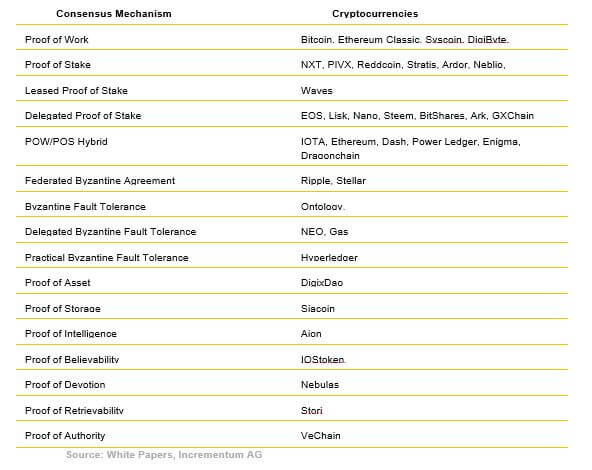
As crypto enthusiasts, we’ve seen the ecosystem evolve with the introduction of Proof of Stake (PoS). PoS swaps out computational power for financial stake, making it a bit like joining an exclusive country club where only those with skin in the game get a say. But wait, there’s more! Enter Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS) and Byzantine Fault Tolerance (BFT)—each bringing their own flair to the consensus party. Are you keeping up, or did we lose you at “delegated”?
Now, this brings us to XRP, the rockstar of the blockchain world, which uses the XRP Ledger Consensus Protocol. Unlike its predecessors, XRP doesn’t rely on mining. Instead, it achieves consensus through a unique protocol that’s faster and more energy-efficient. Imagine a world where transactions settle in seconds rather than minutes or hours. Sounds like a dream, right? Well, XRP is making that dream a reality.
Why does this matter to you, the savvy investor or crypto enthusiast? Because XRP’s consensus mechanism isn’t just about speed and efficiency; it’s about revolutionizing financial transactions. In a world where time is money, XRP ensures you spend less of both. Whether you’re a trader looking for quick settlement times or a fintech professional seeking scalable solutions, XRP’s got your back.
And let’s not forget the environmental impact. In an era where sustainability is paramount, XRP’s low energy consumption is a breath of fresh air. While other cryptocurrencies are busy making headlines for their carbon footprints, XRP is quietly leading the charge towards a greener blockchain future. Isn’t it nice to know you’re investing in something that’s not just good for your wallet, but for the planet too?
As you navigate the ever-evolving world of blockchain technology, remember that understanding these mechanisms is key to making informed investment decisions. From Bitcoin’s resource-heavy PoW to XRP’s sleek, efficient Consensus Protocol, each mechanism has its own strengths and quirks. So why not stay ahead of the curve and keep your crypto knowledge razor-sharp?
At XRP Authority, we pride ourselves on being your go-to source for all things XRP and blockchain. With insights that blend technical depth with a dash of humor, we’re here to guide you through the complexities of the crypto world. Whether you’re an investor, trader, or fintech enthusiast, you can count on us to provide you with the latest news, trends, and insights. So, stick around, because at XRP Authority, we’ve got the expertise you can trust and the wit you’ll enjoy.
Understanding The Evolution of Consensus Mechanisms: From Bitcoin to XRP and Its Impact on XRP

Understanding proof of work and Bitcoin’s foundation
Understanding Proof of Work and Bitcoin’s Foundation
In the beginning, there was proof of work (PoW)—the original consensus mechanism that launched the blockchain revolution into orbit. When Satoshi Nakamoto introduced Bitcoin in 2009, PoW was the linchpin that ensured a decentralized, trustless network could validate transactions without relying on a central authority. It was an elegant solution to a long-standing computer science puzzle: how can strangers agree on a shared ledger without trusting each other or a third party?
Bitcoin’s PoW mechanism works by requiring miners to solve complex mathematical puzzles—think of it as a global Sudoku tournament on steroids. These puzzles are computationally intensive, demanding significant energy and processing power. The first miner to solve the puzzle gets to add the next block of transactions to the blockchain and is rewarded with newly minted bitcoins. This process, known as mining, is both a security feature and an economic incentive model rolled into one.
What makes PoW so foundational is its resistance to manipulation. To tamper with a transaction, an attacker would need to redo the PoW for that block and every block after it, across more than 50% of the network’s computing power—a practically impossible feat at Bitcoin’s scale. This makes PoW highly secure, albeit at a hefty environmental cost.
- Security through computation: PoW’s strength lies in its brute-force approach. The more energy and hash power required, the more secure the network becomes.
- Decentralized validation: Anyone with a computer and internet connection can join the network, validate transactions, and potentially earn rewards.
- Fixed supply economics: Bitcoin’s capped supply of 21 million coins, combined with the halving of miner rewards every four years, creates a deflationary asset model that many investors liken to digital gold.
For early crypto investors, Bitcoin’s PoW model was a proof-of-concept that decentralized finance could work. It disrupted traditional financial systems by removing intermediaries and offering permissionless access to a global monetary network. However, as the network grew, so did its carbon footprint. By 2021, Bitcoin’s energy usage rivaled that of entire countries, sparking debates about sustainability and the need for more efficient consensus mechanisms.
Despite these challenges, Bitcoin remains the bellwether of the crypto market. Its PoW infrastructure is a double-edged sword—providing unmatched security and decentralization at the cost of scalability and energy efficiency. For investors, this means Bitcoin is less about fast transactions and more about long-term value preservation. Its role as a store of value continues to attract institutional capital, even as newer blockchains experiment with greener alternatives.
From a market perspective, Bitcoin often sets the tone. Its price movements influence altcoins, including XRP, which has positioned itself as a high-speed, low-cost alternative for cross-border payments. While Bitcoin’s PoW model laid the groundwork, it also highlighted the need for innovation—spurring the development of more scalable and eco-friendly consensus mechanisms. And that’s where the evolution of blockchain truly takes flight.
The rise of proof of stake and energy efficiency
The Rise of Proof of Stake and Energy Efficiency
As Bitcoin’s proof-of-work model gained traction and notoriety, it also drew criticism for its energy consumption and limited scalability. Enter proof of stake (PoS)—a consensus mechanism designed to address those very issues, offering a more energy-efficient and scalable alternative to traditional mining. Instead of miners battling it out in a computational arms race, PoS networks rely on validators who are chosen to create new blocks based on the number of coins they “stake” or lock up as collateral. In simple terms, the more skin you have in the game, the more likely you are to be selected to validate transactions and earn rewards.
This shift from brute-force computation to economic incentive not only slashes energy usage but also opens the door for a broader range of participants. Validators don’t need expensive mining rigs or access to cheap electricity—just a decent internet connection and a willingness to stake their assets. Ethereum, the second-largest cryptocurrency by market cap, made headlines when it transitioned from PoW to PoS with its long-anticipated “Merge” in 2022. This move reportedly cut its energy consumption by over 99.95%, a statistic that resonated strongly with environmentally conscious investors and institutions.
- Energy efficiency: PoS drastically reduces the carbon footprint of blockchain networks, making them more sustainable and appealing to ESG-focused investors.
- Lower barrier to entry: Without the need for specialized hardware, more users can participate in validation, enhancing decentralization and inclusivity.
- Economic alignment: Validators are incentivized to act honestly—if they misbehave, they risk losing their staked assets, creating a self-regulating ecosystem.
From an investment standpoint, PoS networks offer a unique proposition: yield generation through staking. Rather than relying solely on price appreciation, crypto holders on PoS blockchains can earn passive income by locking up their tokens and supporting network security. This model has given rise to “staking-as-a-service” platforms and DeFi integrations that allow even small-scale investors to participate. For example, Cardano, Polkadot, and Solana—each leveraging variations of PoS—have attracted significant capital not only for their technology but also for their staking incentives and scalability potential.
But while PoS offers clear advantages, it’s not without trade-offs. Critics argue that wealthier participants can dominate validation, leading to centralization risks. Moreover, the security model of PoS is still being tested at scale. Unlike Bitcoin’s battle-hardened PoW, which has weathered over a decade of attacks, PoS is the new kid on the blockchain—promising, but still proving itself in the wild.
For investors, the rise of PoS represents a paradigm shift. It signals a maturing crypto ecosystem that’s responding to both scalability demands and environmental concerns. Networks like Ethereum 2.0 have demonstrated that it’s possible to maintain decentralization and security while dramatically improving efficiency. This innovation cycle is key to crypto’s long-term growth and adoption, especially in sectors like decentralized finance (DeFi), where transaction speed and low fees are non-negotiable.
And yet, even as PoS gains dominance, it’s not the final chapter in the consensus playbook. The evolution continues with hybrid models, delegated systems, and federated consensus protocols—each addressing unique use cases and performance goals. XRP, for example, takes a different route altogether, opting for a federated model that prioritizes speed, scalability, and real-world utility over computational intensity. But more on that in the next section.
For now, it’s clear that PoS has carved out a critical role in blockchain’s evolutionary arc. It embodies the shift from raw computational power to economic game theory—a move that aligns not just with technological progress, but with the values of a more sustainable and inclusive financial future. As crypto matures, expect PoS to remain a cornerstone of innovation, particularly as institutional players seek greener, more scalable blockchain solutions that don’t compromise on security or decentralization.
Delegated consensus models and blockchain governance
Delegated Consensus Models and Blockchain Governance
As blockchain technology evolved beyond the early days of Bitcoin’s energy-hungry mining and Ethereum’s proof-of-stake transformation, a new breed of consensus mechanisms emerged—delegated models. These systems aim to strike a balance between decentralization, performance, and governance by introducing representative validation. Rather than having every node participate in consensus, a select group of trusted or elected validators take on the heavy lifting. Welcome to the world of Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS), Byzantine Fault Tolerance (BFT) variants, and real-time governance innovations that are reshaping the blockchain landscape.
At its core, delegated consensus is about scalability and efficiency without completely abandoning decentralization. Instead of relying on thousands of nodes to reach agreement, the network entrusts a smaller number of validators—chosen by stakeholders or predetermined by protocol rules—to validate transactions and maintain the ledger. This approach dramatically increases throughput and reduces latency, making delegated systems ideal for applications requiring high-speed transaction processing, such as gaming, supply chain logistics, and real-time financial settlements.
- Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS): Popularized by projects like EOS and TRON, DPoS allows token holders to vote for a fixed number of delegates who are responsible for producing blocks. The system is democratic in theory and highly performant in practice, supporting thousands of transactions per second.
- Byzantine Fault Tolerance (BFT) variants: Used in networks like Cosmos and Tendermint, BFT-based consensus mechanisms ensure that the system can tolerate a fraction of malicious actors without compromising consensus. These models are often paired with PoS to enhance security and finality.
- Governance by tokenomics: Delegated models often bake governance directly into the protocol, allowing stakeholders to vote on upgrades, funding proposals, and validator selection—effectively turning blockchain into a self-regulating digital nation-state.
From an investment lens, delegated consensus introduces a new layer of strategic decision-making. Token holders aren’t just passive spectators—they’re voters, influencers, and sometimes even kingmakers. This governance power can impact everything from network fees to development direction, creating dynamic ecosystems where investor alignment and protocol success are intertwined. For example, when a major DPoS network proposes a change to its inflation rate or validator rewards, it’s the token holders who ultimately decide the outcome.
But with great power comes great responsibility—or at least, the potential for centralization. Critics of delegated models argue that they can lead to validator cartels or voter apathy, where a small group of insiders dominate consensus and decision-making. This is especially true when voting participation is low or when large token holders wield disproportionate influence. In some cases, networks have had to implement slashing mechanisms or reward redistribution to maintain fairness and security.
Still, for blockchain projects focused on usability and enterprise adoption, delegated consensus offers a compelling trade-off. It enables real-time processing and governance flexibility while maintaining a level of decentralization that’s acceptable for many use cases. This is particularly relevant in cross-border finance, where speed and compliance are paramount. Investors looking to capitalize on blockchain’s real-world utility should pay close attention to networks utilizing delegated or hybrid consensus models, as they often serve as the backbone for scalable DeFi platforms, payment rails, and tokenized asset ecosystems.
And this brings us closer to XRP and its unique approach. While not a delegated proof-of-stake system per se, the XRP Ledger uses a federated consensus model that shares some of the performance benefits seen in delegated systems, with a twist of its own. The evolution from PoW to PoS and now to delegated and federated models reflects a broader trend: consensus mechanisms are no longer just about securing the network—they’re about enabling usability, governance, and real-world adoption at scale.
As the crypto industry matures, expect delegated consensus systems to play a key role in bridging the gap between decentralized ideals and enterprise-grade performance. For investors, this means looking beyond just the technology and into how governance, validator incentives, and community participation shape the future of a blockchain. Whether you’re eyeing yield opportunities, long-term utility, or governance influence, delegated models offer a rich field for strategic positioning in the next phase of crypto evolution.
The XRP Ledger and federated consensus
The XRP Ledger and Federated Consensus
While much of the blockchain world has been fixated on proof of work and proof of stake, the XRP Ledger (XRPL) takes a bold, alternative route—one that prioritizes speed, reliability, and real-world financial integration. At the heart of this innovation lies the federated consensus mechanism, a system that breaks away from traditional mining and staking models to offer lightning-fast settlement times and minimal energy consumption. In a landscape increasingly focused on sustainability and scalability, XRP’s approach is more than just different—it’s strategic.
The federated consensus model used by XRPL is designed for efficiency. Instead of relying on miners or stakers, the network achieves consensus through a Unique Node List (UNL)—a collection of trusted validators that are agreed upon by network participants. These validators do not compete to solve puzzles or stake coins; they simply agree on the order and validity of transactions through a process of majority voting. If 80% or more of the trusted nodes agree, the ledger advances. It’s fast, deterministic, and final—no lengthy confirmations, no forks, no drama.
- Transaction speed: The XRP Ledger can settle transactions in 3 to 5 seconds, making it one of the fastest blockchains in existence. This speed is a game-changer for financial institutions and payment providers.
- Energy efficiency: With no mining or staking involved, XRPL consumes a fraction of the energy used by PoW or even PoS networks. This makes it an attractive option for ESG-conscious investors and enterprises.
- Deterministic finality: Once a transaction is validated, it’s final. There are no probabilistic confirmations or risk of reorganization, which is critical for high-stakes financial operations.
For investors, the XRP Ledger’s federated consensus is more than just a technical curiosity—it’s a blueprint for real-world adoption. Ripple, the company closely associated with XRP, has forged partnerships with banks, remittance companies, and central banks to bring blockchain into the heart of global finance. The XRPL’s ability to handle high volumes of transactions at low cost positions it as a serious contender for cross-border payments—a market worth trillions of dollars annually.
Unlike many blockchains that struggle with congestion and high fees during peak activity, XRPL maintains consistent performance and costs. Transaction fees are typically fractions of a cent, making microtransactions and high-frequency trading not only possible but practical. This opens the door for use cases ranging from international payroll to decentralized forex markets. Moreover, the ledger has a built-in decentralized exchange (DEX), allowing users to trade assets directly on-chain with minimal friction.
From a market perspective, XRP’s role is uniquely positioned. While Bitcoin is often viewed as digital gold and Ethereum as the foundation for decentralized applications, XRP is carving out a niche as the bridge currency for the internet of value. Its liquidity, speed, and compliance-friendly architecture make it a favorite among institutional players looking to modernize settlement rails without sacrificing regulatory clarity. And with the ongoing development of CBDCs (Central Bank Digital Currencies), the XRPL’s interoperability and scalability could make it a key infrastructure layer in the digital economy of the future.
That said, the federated nature of XRPL does raise questions about decentralization. Critics argue that relying on a curated list of validators introduces centralization risks. However, the XRPL community has made strides in diversifying validator ownership and encouraging participation from independent entities. Unlike traditional financial systems, anyone can run a validator node and propose changes to the UNL, making the network more open than it might initially appear.
For XRP holders and prospective investors, understanding the federated consensus model is crucial. It explains why XRP can offer near-instant settlement at scale, why it’s energy-efficient, and why major financial institutions are piloting solutions built on its rails. It also sheds light on the asset’s price dynamics—when adoption increases, especially in corridors where speed and cost-efficiency matter, demand for XRP as a bridge asset tends to follow.
Technically speaking, the XRPL is a powerhouse. It supports multi-signing, escrow, payment channels, and tokenization—all natively. These features make it not just a payment network but a full-fledged financial toolkit. Developers can build applications ranging from decentralized finance (DeFi) platforms to tokenized securities and NFTs, all while leveraging the performance and reliability of federated consensus.
Looking ahead, the XRPL’s federated consensus mechanism may well become a template for other blockchains seeking to balance performance with security. In a world where real-time payments and digital asset interoperability are becoming the norm, XRPL’s architecture is not just relevant—it’s visionary. For crypto investors, especially those bullish on utility-driven adoption, XRP offers a compelling mix of technological edge and market relevance that’s hard to ignore.
As the blockchain space continues to evolve, federated consensus reminds us that decentralization is not a one-size-fits-all concept. It’s about aligning architecture with purpose. And in the case of XRP, that purpose is clear: to move value as seamlessly as information, across borders, in real time. For savvy investors, this isn’t just a technological evolution—it’s a financial revolution in the making.